Discover the causes and treatments for sudden foot pain without injury. This in-depth guide explores common issues like plantar fasciitis, gout, and stress fractures, providing insights and solutions for unexplained foot discomfort.
Introduction
Sudden foot pain without an apparent injury can be perplexing and concerning. Often, when pain arises without a specific trauma or accident, it can be challenging to pinpoint the exact cause. This comprehensive guide delves into various potential causes, symptoms, and treatment options for unexplained foot pain, shedding light on conditions that might be responsible for your discomfort.
Footwear Issues and Their Impact
One of the most common yet overlooked causes of sudden foot pain is poor footwear. Shoes that are too tight, lack proper arch support, or are worn out can lead to significant discomfort. Footwear issues often manifest as pain in the heels, arches, or toes. Transitioning to well-fitted, supportive shoes can alleviate such pain. Moreover, improper footwear can exacerbate existing conditions like plantar fasciitis or bunions. The link between footwear and foot pain underscores the importance of choosing shoes that fit well and provide adequate support.
Plantar Fasciitis: A Common Culprit
Plantar fasciitis is a prevalent condition that often causes sudden foot pain, particularly in the heel or arch. This condition involves inflammation of the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue running along the bottom of the foot. Individuals may experience sharp, stabbing pain, especially with the first steps in the morning or after prolonged periods of rest. The pain may gradually worsen over time. Treatment typically includes rest, stretching exercises, and using orthotic devices to support the arch and alleviate stress on the plantar fascia.
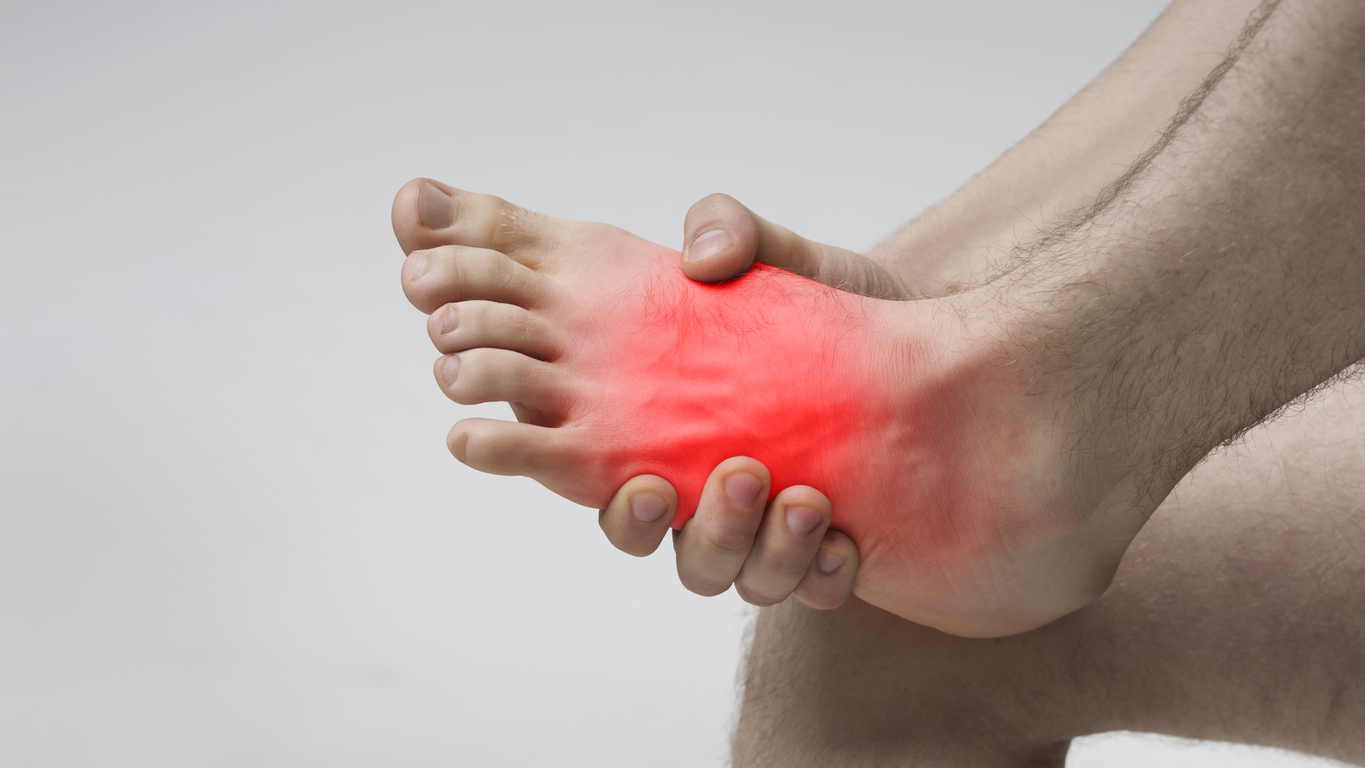
The Role of Gout in Sudden Foot Pain
Gout is a type of arthritis that can cause sudden and severe pain in the joints, frequently affecting the big toe. This condition results from the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints, leading to intense pain, swelling, and redness. Gout attacks can be triggered by dietary factors, dehydration, or underlying health conditions. Managing gout involves medication to reduce uric acid levels and lifestyle modifications such as dietary changes and increased hydration. Understanding the triggers and symptoms of gout can help in managing and preventing future attacks.
Nerve-Related Pain: Morton’s Neuroma and Beyond
Nerve-related issues, such as Morton’s neuroma, can lead to sudden foot pain. Morton’s neuroma involves the thickening of nerve tissue between the toes, often resulting in a sharp, burning sensation or pain in the ball of the foot. This condition can be aggravated by high heels or tight shoes. Treatment usually includes changing footwear, using orthotics, and in some cases, corticosteroid injections or surgery. Identifying and addressing nerve-related pain is crucial for effective management and relief.

Stress Fractures: Small Cracks with Big Impact
Stress fractures are tiny cracks in the bones of the foot that develop due to repetitive stress or overuse. They can cause sudden pain, often worsening with activity and improving with rest. Stress fractures are common among athletes or individuals who suddenly increase their physical activity. Diagnosis typically involves imaging tests, and treatment focuses on rest, immobilization, and gradual return to activity. Understanding the signs of stress fractures can aid in early detection and prevent further complications.
Tendinitis: Inflammation and Pain
Tendinitis, or inflammation of the tendons, can lead to sudden foot pain. This condition often results from overuse or strain on the tendons, such as those in the Achilles or posterior tibial areas. Pain may be localized to the affected tendon and can be exacerbated by movement or activity. Managing tendinitis involves rest, ice application, and anti-inflammatory medications. Strengthening exercises and proper footwear can also aid in recovery and prevent recurrence.
Infections and Foot Pain
Infections, whether bacterial or fungal, can cause sudden foot pain accompanied by swelling, redness, or warmth. Conditions like cellulitis or athlete’s foot might present with these symptoms. Prompt treatment with antibiotics or antifungal medications is essential for addressing infections. Maintaining good foot hygiene and addressing infections early can prevent more severe complications and alleviate pain.
Circulatory Problems and Foot Discomfort
Circulatory issues, such as poor blood flow or blood clots, can contribute to sudden foot pain. These conditions may cause discomfort, swelling, and changes in skin color. Identifying circulatory problems often requires medical evaluation, including imaging studies and blood tests. Treatment focuses on improving circulation, which may involve medication, lifestyle changes, or medical interventions.
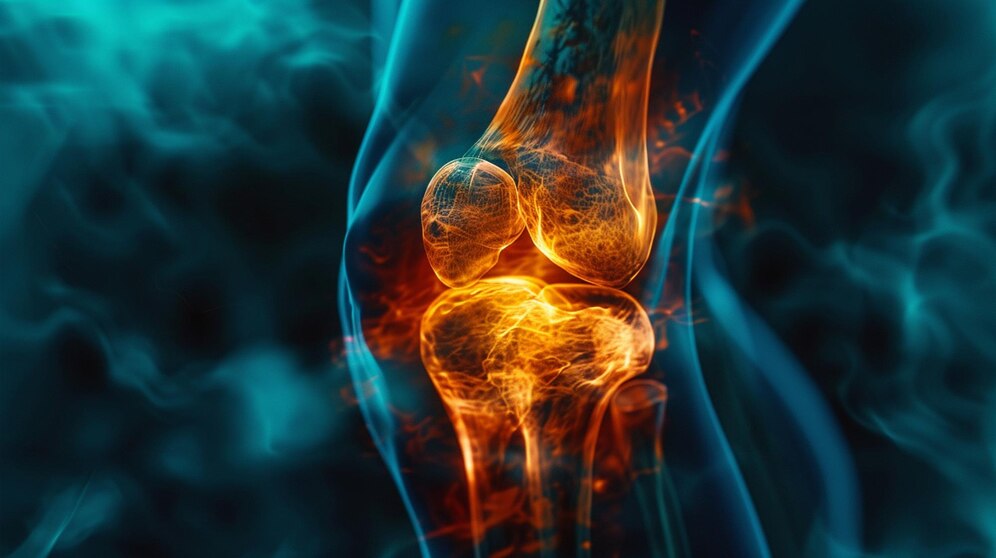
Arthritis and Its Effects on the Feet
Various forms of arthritis, including osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, can cause sudden foot pain. Arthritis-related pain often involves joint inflammation, stiffness, and swelling. Managing arthritis involves medications to reduce inflammation, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications to support joint health. Understanding the impact of arthritis on the feet is crucial for effective pain management and maintaining mobility.
Bunions and Their Impact on Foot Health
Bunions are bony bumps that form at the base of the big toe, leading to pain and discomfort. They can develop gradually and become painful due to changes in foot structure or pressure from footwear. Treatment options include changes in footwear, orthotic devices, and in some cases, surgical intervention. Addressing bunions early can prevent further complications and improve foot comfort.

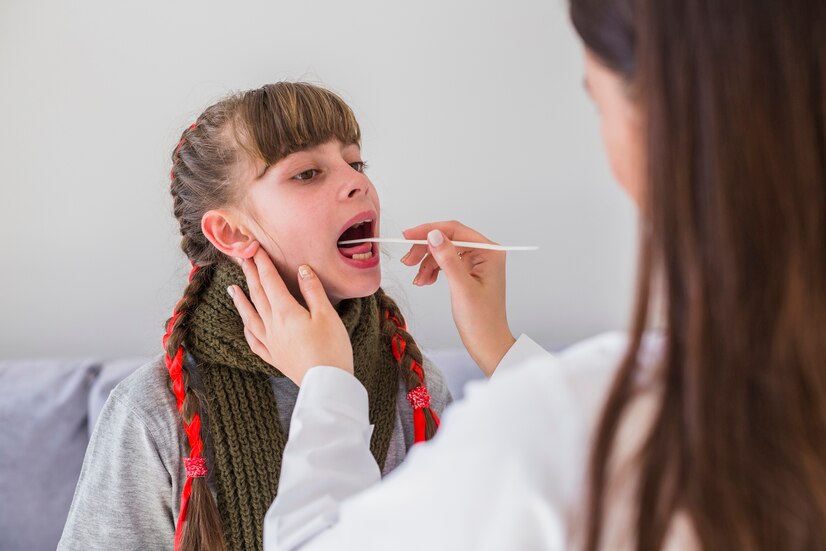
Evaluating Sudden Foot Pain: Diagnostic Approaches
When experiencing sudden foot pain without a clear injury, a thorough diagnostic approach is essential. This process may involve a detailed medical history, physical examination, and imaging studies such as X-rays or MRIs. Identifying the underlying cause of the pain is crucial for developing an effective treatment plan and addressing any contributing factors.
Treatment Strategies for Unexplained Foot Pain
Effective treatment for sudden foot pain without injury depends on the underlying cause. Common strategies include rest, ice application, anti-inflammatory medications, and physical therapy. In some cases, specialized treatments such as injections or surgery may be necessary. Tailoring the treatment approach to the specific condition can enhance recovery and alleviate pain.
Preventive Measures for Foot Pain
Preventing sudden foot pain involves adopting healthy habits and making lifestyle changes. Wearing supportive footwear, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding excessive physical stress on the feet are key preventive measures. Regular foot exercises and proper foot hygiene can also contribute to long-term foot health and reduce the risk of pain.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While some cases of sudden foot pain may resolve with self-care measures, others may require professional medical attention. Seeking medical advice is essential if the pain is severe, persistent, or accompanied by other symptoms such as swelling, redness, or difficulty walking. A healthcare professional can provide a comprehensive evaluation and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Coping with Chronic Foot Pain
For individuals experiencing chronic foot pain, coping strategies and lifestyle adjustments can improve quality of life. Managing chronic pain often involves a combination of medical treatment, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes. Supportive devices, pain management techniques, and psychological support can also play a role in coping with long-term foot discomfort.
Understanding the Psychological Impact of Foot Pain
Foot pain, especially when sudden and unexplained, can have a psychological impact on individuals. Anxiety, stress, and frustration related to pain can affect overall well-being. Addressing the psychological aspects of foot pain, alongside physical treatment, can contribute to a more holistic approach to managing discomfort and improving quality of life.
Future Directions in Foot Pain Research
Ongoing research into foot pain aims to enhance understanding and treatment options for various conditions. Advances in medical technology, diagnostic techniques, and treatment methods hold promise for more effective management of sudden foot pain. Staying informed about emerging research and treatment options can offer new avenues for addressing unexplained foot discomfort.
Conclusion
Sudden foot pain without an apparent injury can arise from a variety of causes, ranging from footwear issues to underlying medical conditions. Understanding the potential causes, diagnostic approaches, and treatment options is crucial for effectively managing and alleviating foot pain. Whether through self-care measures, professional medical intervention, or lifestyle adjustments, addressing the underlying issues can lead to improved comfort and overall foot health.
Read also: Exercises for ACL Tear Without Surgery